Unprecedented Simultaneous Heat Waves
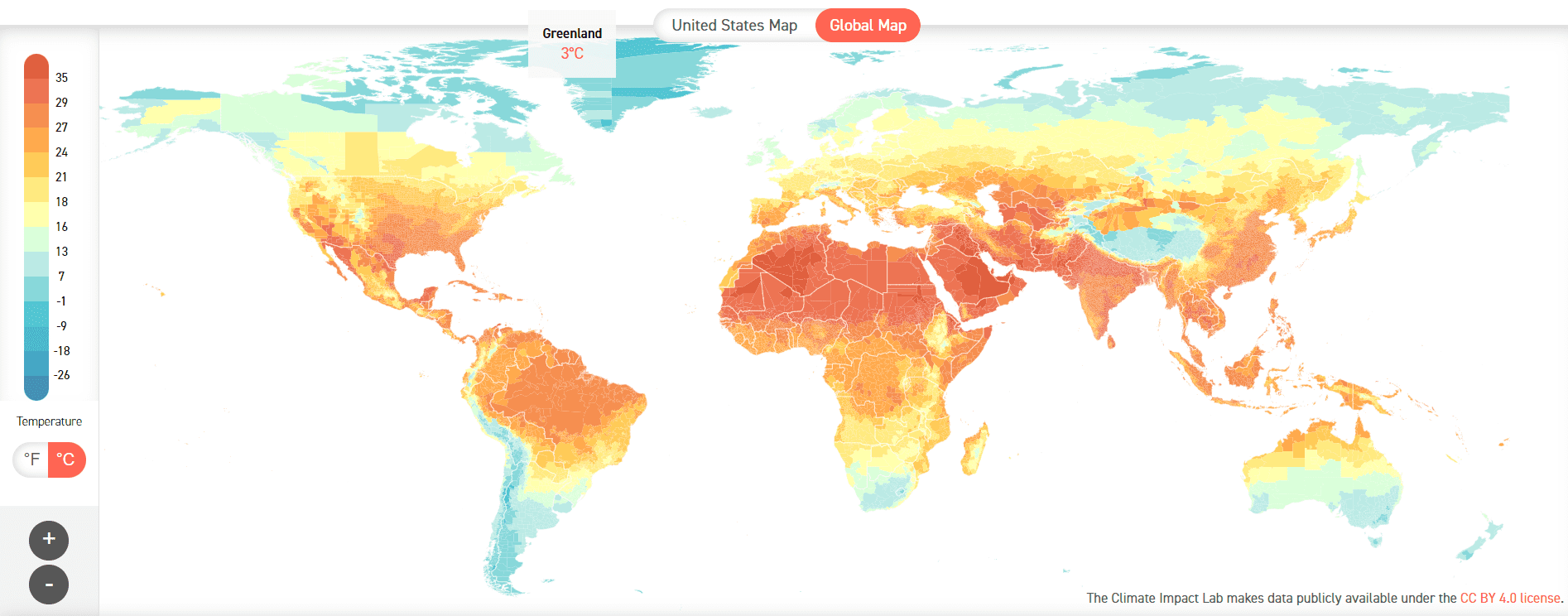
The world is witnessing an alarming trend in recent years, where heat waves have struck multiple regions simultaneously, wreaking havoc on communities, economies, and the environment. In July 2023, China, southern Europe, and the United States are grappling with one of the worst heat waves on record, underscoring the intensifying impact of climate change. These extreme weather events, occurring concurrently in different parts of the Northern Hemisphere, are a stark reminder of the urgent need to address climate change and its associated risks from a business risk management perspective.
Climate change-induced heat waves pose significant challenges for businesses worldwide, exposing them to a multitude of risks. From disrupted supply chains and damaged physical assets to heightened financial market vulnerabilities, the effects of extreme heat are far-reaching and multifaceted. As these events become more frequent and intense, businesses must proactively adapt their risk management strategies to navigate the changing landscape of climate-related risks.
Climate Impact Lab Next 20 Years 2020-2039 – Global Map
Climate Change Impacts and Business Risks
Extreme weather events, like heat waves, are becoming more commonplace due to climate change. Rising global temperatures lead to prolonged periods of intense heat, putting immense pressure on businesses across various sectors. Agriculture faces reduced crop yields and increased water scarcity, impacting food supply chains. The energy sector confronts challenges in maintaining power generation, distribution, and cooling systems during extreme heat, leading to potential service disruptions and outages. Moreover, heat waves can trigger health and productivity issues for the workforce, further straining business operations.
Assessing Vulnerabilities in Infrastructure
Physical asset risks are a paramount concern for businesses in regions prone to heat waves. High temperatures can induce stress on infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, leading to structural damage and increased maintenance expenses. In urban areas, excessive heat exacerbates the “urban heat island” effect, where buildings and concrete retain heat, intensifying local temperatures and compromising public health and energy demands. Businesses must conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify vulnerable assets and develop adaptation plans to safeguard critical infrastructure from heat wave impacts. Embracing sustainable building practices and implementing green infrastructure solutions can help mitigate heat-related risks and enhance overall resilience.
Financial Market Vulnerabilities
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events poses substantial risks to the financial markets. Insurance companies face mounting claims from businesses and individuals affected by heat wave-related damages. These escalating costs could lead to higher premiums, making insurance coverage less affordable for businesses, thereby increasing their financial exposure. Moreover, the financial industry faces potential risks from investments in carbon-intensive assets, which may become stranded as the global transition to a low-carbon economy accelerates. Investors are increasingly factoring climate risks into their decisions, and businesses with inadequate climate resilience may experience reduced investment interest and valuations.
Regulatory Landscape and Investor Demands for Sustainable Business
In response to the escalating climate crisis, governments worldwide are enacting new regulations and policies aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices. Businesses operating in affected regions must keep abreast of these changing regulatory landscapes to remain compliant and avoid potential penalties. Additionally, evolving regulations may create opportunities for businesses to invest in clean technologies, renewable energy sources, and energy-efficient processes, leading to cost savings and competitive advantages. However, compliance can also impose financial burdens, particularly on industries heavily reliant on fossil fuels. As such, proactive engagement with policymakers and industry associations becomes essential to influence the development of practical and equitable climate policies.
The Rise of ESG Investing
Investors are increasingly prioritising environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their investment decisions. They seek not only financial returns but also assurance that their investments align with sustainable and ethical practices. As a result, companies with strong ESG performance are more likely to attract investment and secure capital at favorable terms. Conversely, those neglecting ESG considerations may experience difficulty accessing capital and may face higher borrowing costs. Incorporating ESG principles into business strategies is thus paramount for sustained financial success in a world where responsible investing is gaining momentum.
Integrating ESG Principles for Financial Advantage
To align with investor expectations and attract sustainable capital, businesses must integrate ESG principles into their core operations and decision-making processes. Prioritising environmental initiatives, such as reducing carbon emissions, conserving water resources, and minimising waste, showcases a commitment to addressing climate risks and promoting resource efficiency. Socially responsible practices, such as fostering diversity and inclusion, ensuring fair labor practices, and prioritising community engagement, enhance a company’s reputation and strengthen stakeholder trust. Effective governance practices, including transparent reporting and robust risk management frameworks, demonstrate accountability and risk oversight, further bolstering investor confidence.
Strategic Planning for Climate Resilience
Preparing for an Uncertain Climate Future
As climate change continues to unfold, uncertainties abound regarding its precise impacts on businesses and economies. To prepare for an uncertain climate future, businesses must engage in comprehensive scenario analysis, assessing various climate-related risks and their potential severity. This exercise enables businesses to identify vulnerabilities, prioritise action areas, and allocate resources effectively. Collaborating with climate scientists, researchers, and risk experts can provide invaluable insights into regional climate trends and potential impacts on operations, supply chains, and markets.
Strategic Decision-making for Climate Resilience
Climate resilience requires a holistic approach to decision-making, involving senior leadership, board members, and stakeholders. Integrating climate considerations into corporate governance enables businesses to proactively address risks and capitalise on opportunities in a rapidly changing landscape. Strategic decisions may involve investing in infrastructure upgrades to withstand extreme weather events, diversifying supply chains to reduce exposure to climate-sensitive regions, and innovating products and services to cater to changing consumer demands. Additionally, businesses can foster a culture of climate-consciousness among employees, encouraging sustainable practices throughout the organisation and reinforcing the commitment to climate resilience.
Climate Risk Mitigation
Engaging Stakeholders for Sustainable Solutions
Climate action extends beyond businesses and governments; it requires collaboration with a broad range of stakeholders, including consumers, investors, NGOs, and local communities. Engaging with these stakeholders fosters transparency, builds trust, and enhances the credibility of sustainability efforts. Listening to consumer demands for sustainable products and services can drive innovation and lead to new market opportunities. Collaboration with NGOs can leverage their expertise and resources to address environmental and social challenges. Supporting local communities through sustainable initiatives creates positive impacts, promoting long-term goodwill and fostering a sense of shared responsibility in the fight against climate change. By embracing collaborative approaches, businesses can catalyse systemic change and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future.
Preparing for Climate-Related Losses
As climate risks escalate, businesses face growing threats of property damage, supply chain disruptions, and operational interruptions. Insurance can play a critical role in helping businesses manage climate-related risks and mitigate potential losses. However, the traditional insurance approach may not fully encompass all climate risks. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses to conduct thorough risk assessments, including climate scenario analysis, to identify uninsured or underinsured exposures. Armed with a clear understanding of their risk profile, businesses can work closely with insurers to design comprehensive insurance packages tailored to their specific needs.
Closing the Climate Risk Management Gap
As extreme weather events become more frequent, businesses face escalating risks, from financial vulnerabilities in the market to disrupted supply chains and damaged infrastructure. Adapting to shifting regulatory landscapes, embracing sustainable practices, and integrating ESG principles are vital for businesses to navigate the transition to a low-carbon economy successfully. Strategic planning, collaboration, and innovative insurance solutions play key roles in building climate resilience. It is clear that climate change and sustainability risks are no longer distant concerns; they demand immediate, proactive action from businesses to ensure a more sustainable, resilient future.